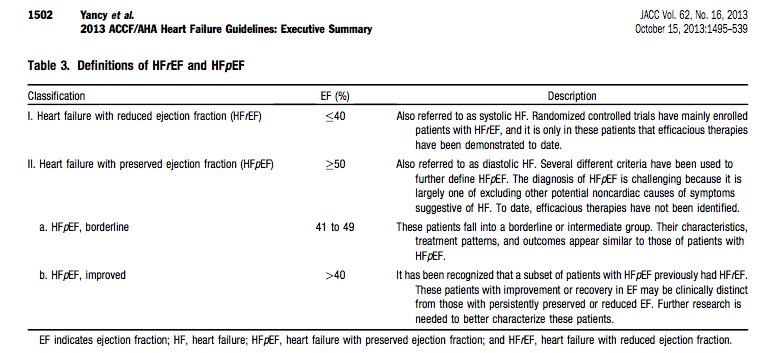
#FITSurvivalGuide #tweetorial Diagnosis of Heart failure: HF is a complex clinical syndrome related to structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or contraction. HF can be classified into HFrEF and HFpEF based on assessment of LVEF. 
Typical HF symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, edema, orthopnea, PND. NYHA system used to indicate symptom severity. Essential to inquire about onset, duration & progression of symptoms, risk factors for HF (MI, HTN, DM), FH of HF, drug or alcohol abuse, radiation/chemotherapy. 

HF is a largely clinical diagnosis. Physical exam must include careful assessment of vital signs, signs of volume overload (JVD, edema, S3, rales on lung exam) and assessment of perfusion (cyanosis, cool extremities). 
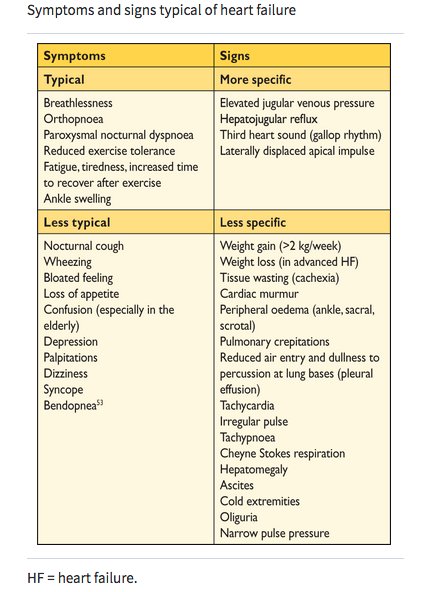
For acute or chronic decompensated HF, it is very important to recognize severity of the decompensated state based on degree of congestion and perfusion. Narrow pulse pressure, tachycardia, cool extremities, poor urine output and confusion are harbingers of cardiogenic shock. 

Diagnostic tests for HF: Labs (CBC, CMP, HbA1c, lipids, TSH), EKG (e/o prior MI, voltage, AF, arrhythmias). Serum lactate as marker of perfusion. Testing for etiology of non-ischemic cardiomyopathy: screening for hemochromatosis, HIV, amyloidosis, pheochromocytoma, rheum disease.
BNP is used for diagnosis, prognosis and follow up in HF. Patients with normal BNP levels are unlikely to have HF. BNP > 100 pg/mL, NT-proBNP > 300 pg/mL in an acute setting is abnormal. Can be falsely elevated in AF, old age and renal failure, and falsely low in obese patients.
Imaging for new-onset or decompensated HF: CXR for heart size & pulmonary congestion. Echo to assess systolic and diastolic LV & RV fn, size, thickness, RWM, valve fn, LA volume, filling pr (E/e’). Repeat echo if clinical status changes or to assess improvement after GDMT.
Stress testing can help diagnose myocardial ischemia, viability and diastolic dysfunction in new onset HF. If ischemic etiology suspected, LHC for pts eligible for revascularization. Endomyocardial biopsy useful when a specific diagnosis is suspected that would influence therapy.
CMR is the gold standard for measurements of volumes, mass and EF. Can assess myocardial fibrosis using LGE & aid in establishing etiology; ischemic vs. non-ischemic origin of HF (myocarditis, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, Fabry disease, non-compaction and hemochromatosis).
RHC can help guide therapy in select acute HF pts whose fluid status, perfusion, or vascular resistance is uncertain; non responders to std therapy; worsening renal function; who require parenteral vasoactive agents; or who may need consideration for MCS or transplantation.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh