1/11
A #tweetorial on Syncope #FITsurvivalguide
Definition:
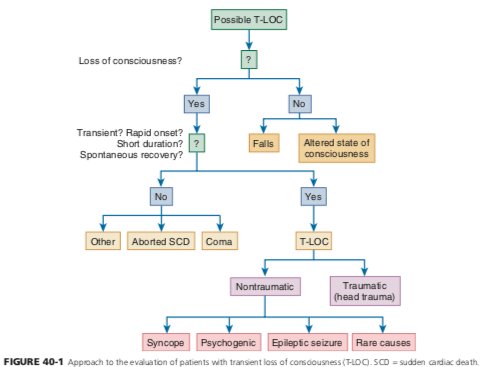
Sudden transient loss of consciousness with associated loss of postural tone, spontaneous recovery without neurologic deficits
The key is in the H&P
A good H&P can provide a dx in up to 50% of cases.

A #tweetorial on Syncope #FITsurvivalguide
Definition:
Sudden transient loss of consciousness with associated loss of postural tone, spontaneous recovery without neurologic deficits
The key is in the H&P
A good H&P can provide a dx in up to 50% of cases.

2
Goals.
1. Determine specific cause; this will direct therapy, prevent recurrences, ⬇️ expensive evaluations, and improve outcome.
2. Determine presence of cardiac syncope which portends ⬆️ mortality and sudden death.
3. Identify those who will benefit Inpt 🆚 outpt eval
Goals.
1. Determine specific cause; this will direct therapy, prevent recurrences, ⬇️ expensive evaluations, and improve outcome.
2. Determine presence of cardiac syncope which portends ⬆️ mortality and sudden death.
3. Identify those who will benefit Inpt 🆚 outpt eval
3/11
History
- Most important >> circumstance of syncope (ie. Prodrome), associated with particular activity? Exertion? change in position?
- Assess for sx of vasovagal syncope (most common cause)
- Duration of event
- Residual symptoms



History
- Most important >> circumstance of syncope (ie. Prodrome), associated with particular activity? Exertion? change in position?
- Assess for sx of vasovagal syncope (most common cause)
- Duration of event
- Residual symptoms




4/11
Initial exam
- search for presence of structural heart disease Valvular stenosis, CM, or MI >> Inc risk of malignant arrhythmia.
- Fundoscopic exam - ?embolism
- ?Carotid bruit
- Subtle neurologic deficits - ?stroke or neuropathy


Initial exam
- search for presence of structural heart disease Valvular stenosis, CM, or MI >> Inc risk of malignant arrhythmia.
- Fundoscopic exam - ?embolism
- ?Carotid bruit
- Subtle neurologic deficits - ?stroke or neuropathy



5/11
- Orthostatics ( +ve if ⬇️ systolic BP from baseline value > 20 mmHg or diastolic BP > 10 mmHg, HR ⬆️ >10BPM)
- Electrocardiogram

- Orthostatics ( +ve if ⬇️ systolic BP from baseline value > 20 mmHg or diastolic BP > 10 mmHg, HR ⬆️ >10BPM)
- Electrocardiogram


6/11
Based on initial findings, additional tests may be performed when needed
- ECG monitoring when there is a suspicion of arrhythmic syncope.
- Echo when known h/o or ?❤️ dz
- ?Carotid hypersensitivity - Carotid sinus massage
- ?Reflex syncope - Tilt table
Based on initial findings, additional tests may be performed when needed
- ECG monitoring when there is a suspicion of arrhythmic syncope.
- Echo when known h/o or ?❤️ dz
- ?Carotid hypersensitivity - Carotid sinus massage
- ?Reflex syncope - Tilt table

7/11
- Blood tests when clinically indicated
- ?Hemorrhage - H/H
- ?Hypoxia - O2 Sat & ABG
- ?Cardiac ischemia - Troponins
- ?PE - D-Dimer
- Blood tests when clinically indicated
- ?Hemorrhage - H/H
- ?Hypoxia - O2 Sat & ABG
- ?Cardiac ischemia - Troponins
- ?PE - D-Dimer
8/11
- Exercise stress test considered if Sx assoc. w/ exertion
- Outpt ❤️ monitoring- Holter/loop rec - High clinical suspicion for underlying arrhythmia without clear diagnosis.
- EPS - Considered in patients with underlying structural ❤️ dz. ? origin of wide complex tach.
- Exercise stress test considered if Sx assoc. w/ exertion
- Outpt ❤️ monitoring- Holter/loop rec - High clinical suspicion for underlying arrhythmia without clear diagnosis.
- EPS - Considered in patients with underlying structural ❤️ dz. ? origin of wide complex tach.

9/1
Mgmt:
- Goal: Preventing recurrent episodes and ⬇️ mortality
- Educate pts; avoid triggers, maintain appropriate vol. avoid vasodilator therapy. mod exercise. private 🚗? see imgs
- 🛑 unnecessary meds
- Electrolyte abnormality corrected if suspected as cause of arrhythmia


Mgmt:
- Goal: Preventing recurrent episodes and ⬇️ mortality
- Educate pts; avoid triggers, maintain appropriate vol. avoid vasodilator therapy. mod exercise. private 🚗? see imgs
- 🛑 unnecessary meds
- Electrolyte abnormality corrected if suspected as cause of arrhythmia



10/11
- Antiarrhytmic therapy in confirmed arrhythmic syncope
- EPS with ablation in drug refractory malignant arrhythmia
- Device therapy for bradyarrhythmias or high degree conduction abnormality. ICD for malignant arrhythmia
- Surgical tx - Outflow tract obstruction - HCM
- Antiarrhytmic therapy in confirmed arrhythmic syncope
- EPS with ablation in drug refractory malignant arrhythmia
- Device therapy for bradyarrhythmias or high degree conduction abnormality. ICD for malignant arrhythmia
- Surgical tx - Outflow tract obstruction - HCM
11
Recommended reading
- 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for evaluation and management of syncope
- 2018 ESC guidelines for dx and management of syncope

Recommended reading
- 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for evaluation and management of syncope
- 2018 ESC guidelines for dx and management of syncope


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh